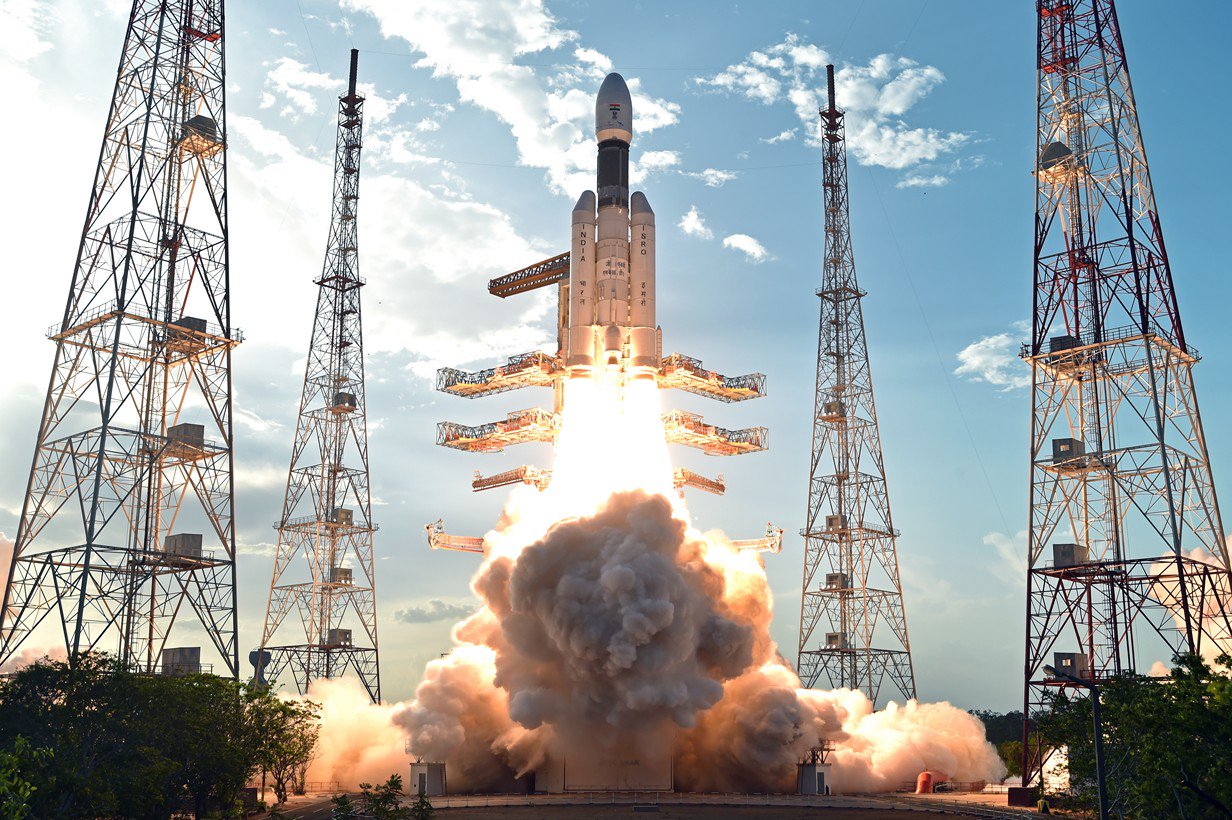
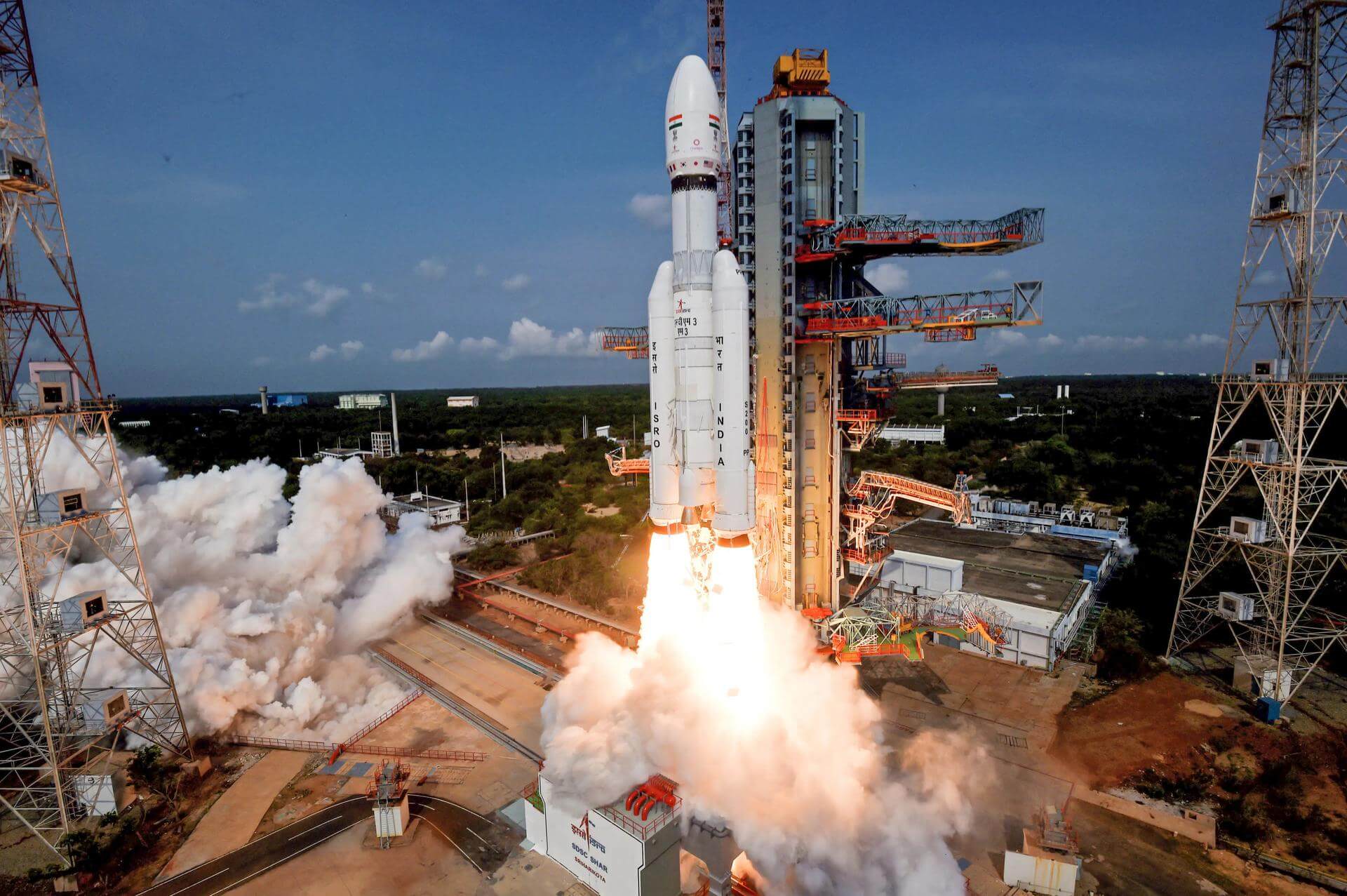
LVM-3 (GSLV Mk III)
ActiveIndian Space Research Organization (ISRO)
Dec. 18, 2014
Description
The Launch Vehicle Mark-3 (LVM-3), previously called Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark III (GSLV Mk III), is a three-stage medium-lift launch vehicle developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). It is designed to launch satellites into geostationary orbit, and is intended as a launch vehicle for crewed missions under the Indian Human Spaceflight Programme.
Specifications
-
Max Stage
3 -
Length
43.4 m -
Diameter
4.0 m -
Fairing Diameter
― -
Launch Mass
629 T -
Thrust
11898 kN -
Apogee (Sub-Orbital)
40000 km
Family
-
Name
LVM-3 (GSLV Mk III) -
Family
― -
Variant
― -
Alias
― -
Full Name
Launch Vehicle Mark-3 (GSLV Mk III)
Payload Capacity
-
Launch Cost
$46000000 -
Low Earth Orbit
10000 kg -
Geostationary Transfer
Orbit
5000 kg -
Direct Geostationary
― -
Sun-Synchronous Capacity
―
Indian Space Research Organization
Government
Chairman: S. Somanath
ISRO 1969The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) is the space agency of the Government of India headquartered in the city of Bangalore. Its vision is to "harness space technology for national development while pursuing space science research and planetary exploration."
Upcoming Spaceflights
LVM-3 | Gaganyaan-1
Indian Space Research Organization | IndiaSatish Dhawan Space Centre, India
TBD July, 2024
LVM-3 | Gaganyaan-2
Indian Space Research Organization | IndiaSatish Dhawan Space Centre, India
TBD December, 2024
LVM-3 | Gaganyaan-3
Indian Space Research Organization | IndiaSatish Dhawan Space Centre, India
TBD December, 2025
LVM-3 | Chandrayaan-3
Indian Space Research Organization | IndiaSatish Dhawan Space Centre, India
July 14, 2023, 9:05 a.m.
Status: Launch Successful
Mission:
Chandrayaan-3 is India's third mission to the Moon. It repeats most of the failed Chandrayaan-2 mission, with only a lander and rover. After a controlled descent, the lander will perform a soft landing on the lunar surface at a specified site and deploy the rover. The six-wheeled rover weighs around 20 kg and will operate on solar power. It will move around the landing site, performing lunar surface chemical analysis and relaying data back to Earth through the orbiter. The lander will be collecting data on Moon-quakes, thermal properties of the lunar surface, the density and variation of lunar surface plasma. Altogether, the Chandrayaan-3 mission will collect scientific information on lunar topography, mineralogy, elemental abundance, lunar exosphere and signatures of hydroxyl and water-ice.
Lunar OrbitLVM-3 | OneWeb 18
Indian Space Research Organization | IndiaSatish Dhawan Space Centre, India
March 26, 2023, 3:30 a.m.
Status: Launch Successful
Mission:
A batch of 36 satellites for the OneWeb satellite constellation, which is intended to provide global Internet broadband service for individual consumers. The constellation is planned to have around 648 microsatellites (of which 60 are spares), around 150 kg each, operating in Ku-band from low Earth orbit.
Polar OrbitLVM-3 | OneWeb 14
Indian Space Research Organization | IndiaSatish Dhawan Space Centre, India
Oct. 22, 2022, 6:37 p.m.
Status: Launch Successful
Mission:
A batch of 36 satellites for the OneWeb satellite constellation, which is intended to provide global Internet broadband service for individual consumers. The constellation is planned to have around 648 microsatellites (of which 60 are spares), around 150 kg each, operating in Ku-band from low Earth orbit.
Polar OrbitLVM-3 | Chandrayaan-2
Indian Space Research Organization | IndiaSatish Dhawan Space Centre, India
July 22, 2019, 9:13 a.m.
Status: Launch Successful
Mission:
Chandrayaan-2 is India's second mission to the Moon. It consists of an orbiter, lander and rover. After reaching the 100 km lunar orbit, the lander housing the rover will separate from the orbiter. After a controlled descent, the lander will perform a soft landing on the lunar surface at a specified site and deploy the rover. Six-wheeled rover weighs around 20 kg and will operate on solar power. It will move around the landing site, performing lunar surface chemical analysis and relaying data back to Earth through the orbiter. The lander will be collecting data on Moon-quakes, thermal properties of the lunar surface, the density and variation of lunar surface plasma. The orbiter will be mapping lunar surface. Altogether, Chandrayaan-2 mission will collect scientific information on lunar topography, mineralogy, elemental abundance, lunar exosphere and signatures of hydroxyl and water-ice.
Lunar OrbitLVM-3 | GSAT-29
Indian Space Research Organization | IndiaSatish Dhawan Space Centre, India
Nov. 14, 2018, 11:38 a.m.
LVM-3 | GSAT-19
Indian Space Research Organization | IndiaSatish Dhawan Space Centre, India
June 5, 2017, 11:58 a.m.
Status: Launch Successful
Mission:
GSAT-19 is an Indian geostationary communications satellite. With a mass of 3200 kg and expected operational lifetime of 15 years, this satellite will test several epxerimental technologies like electrical propulsion, deployable thermal radiatiors, indigenious Li-Ion batteries.
Geostationary Transfer OrbitLVM-3 | CARE (Demo Flight)
Indian Space Research Organization | IndiaSatish Dhawan Space Centre, India
Dec. 18, 2014, 4 a.m.
Status: Launch Successful
Mission:
The CARE is a mock-up of the planned Indian crewed space capsule. Its mission is to study re-entry and thermal behaviour. CARE does not have the pressure-vessel of the final capsule, but is only a structural mock-up. It will re-enter and land in the bay of Bengal to be retrieved. For the suborbital flight, it is mounted upside-down inside the payload fairing. This launch uses a non-functional 2nd stage. CARE separates from the launch vehicle after 1st stage shutdown.
SuborbitalFalcon 9
Starlink Group 6-57
Space Launch Complex 40 - Cape Canaveral, FL, USAA batch of 23 satellites for the Starlink mega-constellation - SpaceX's project for space-based Internet communication system.
Long March 5
Chang'e 6
101 - Wenchang Space Launch Site, People's Republic of ChinaChang'e 6/CE-6 is scheduled to launch in 2024 to return samples from the Far Side of the Moon (near southern edge of the Apollo Basin) for the first …
SR75
Maiden Flight
Pad 1 - Koonibba Test Range, South AustraliaTest flight of HyImpulse's SR75 sounding rocket
Falcon 9
Starlink Group 6-55
Space Launch Complex 40 - Cape Canaveral, FL, USAA batch of 23 satellites for the Starlink mega-constellation - SpaceX's project for space-based Internet communication system.
Falcon 9
WorldView Legion 1 & 2
Space Launch Complex 4E - Vandenberg SFB, CA, USAWorldView Legion is a constellation of Earth observation satellites built and operated by Maxar. Constellation is planned to consist of 6 satellites …