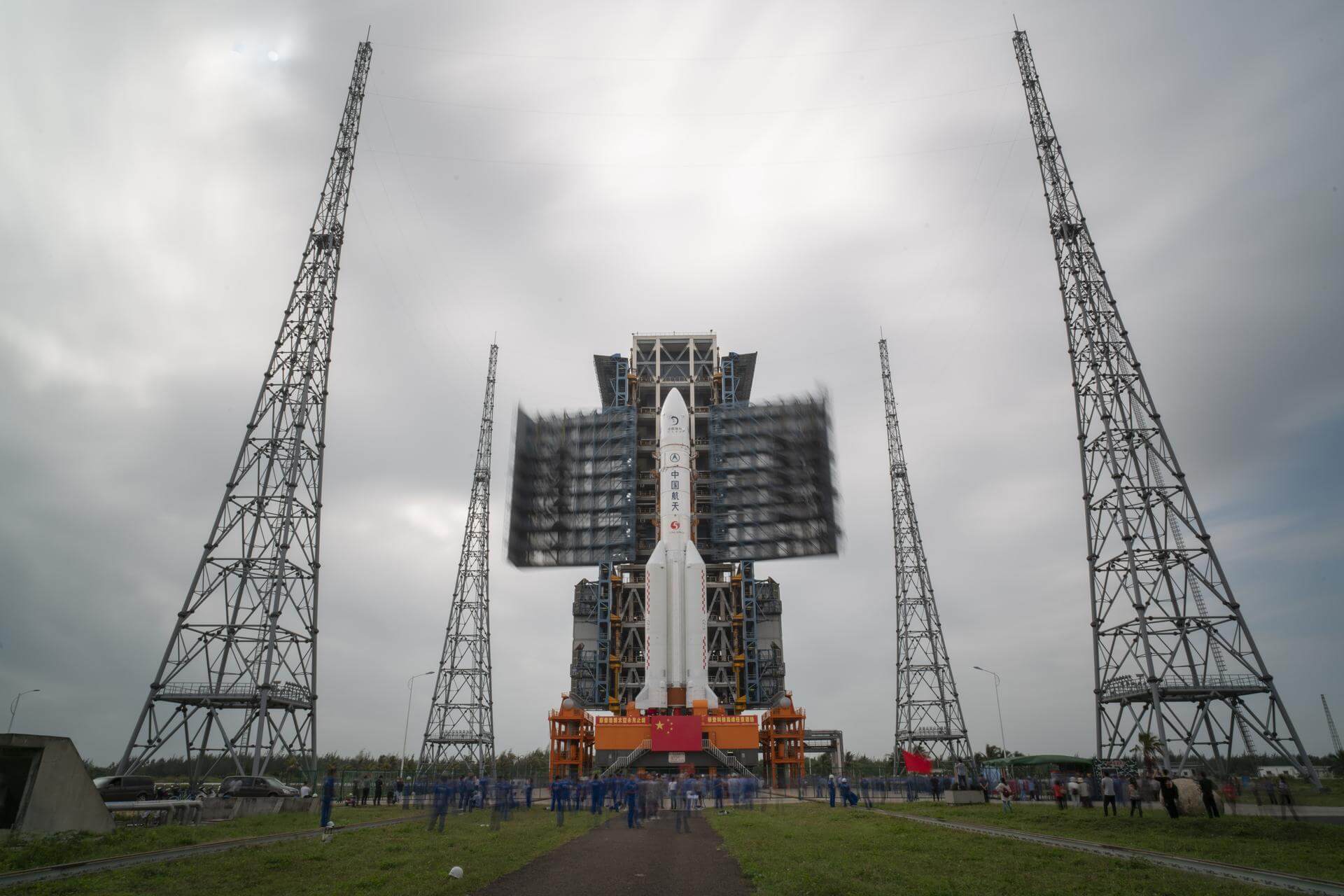
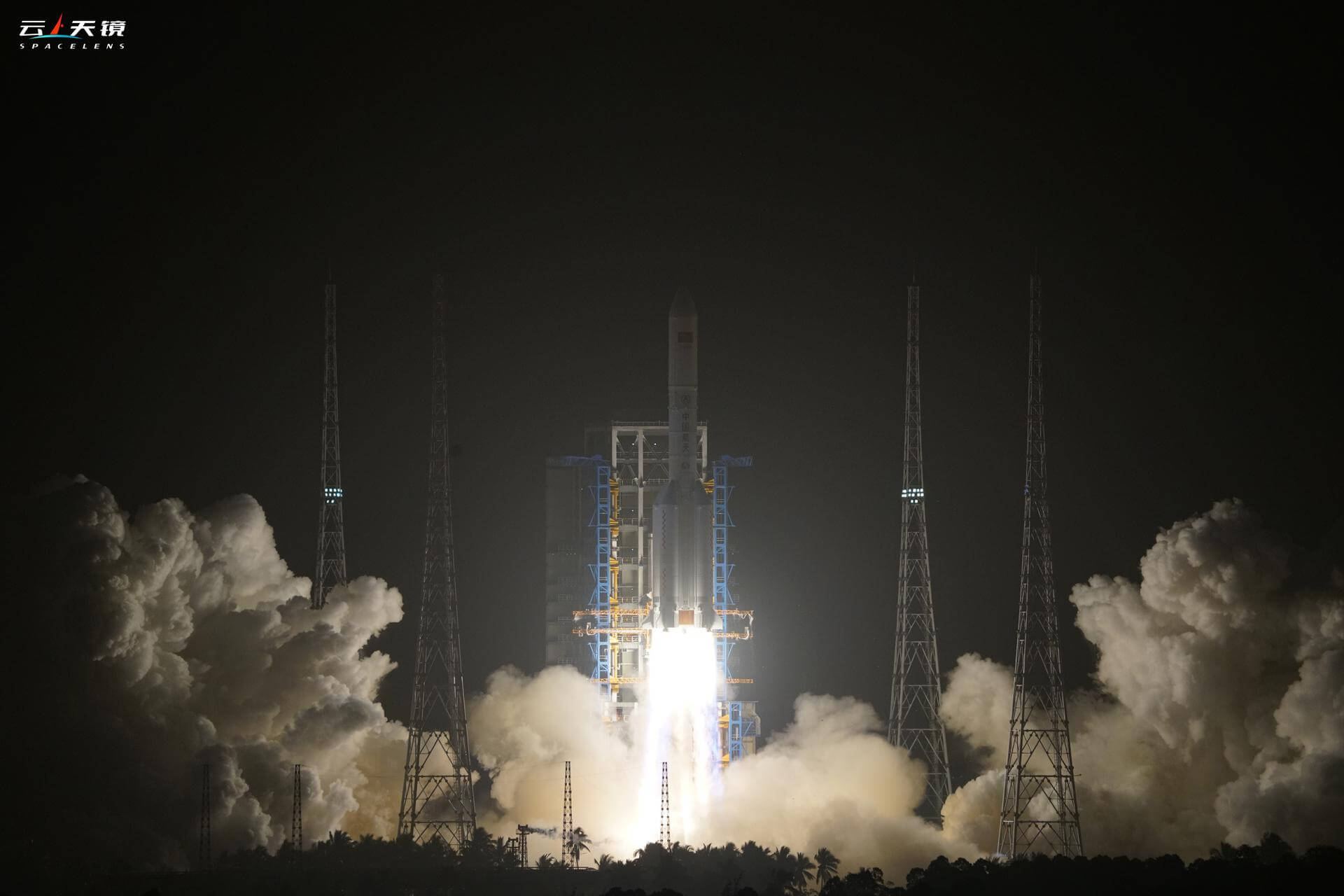
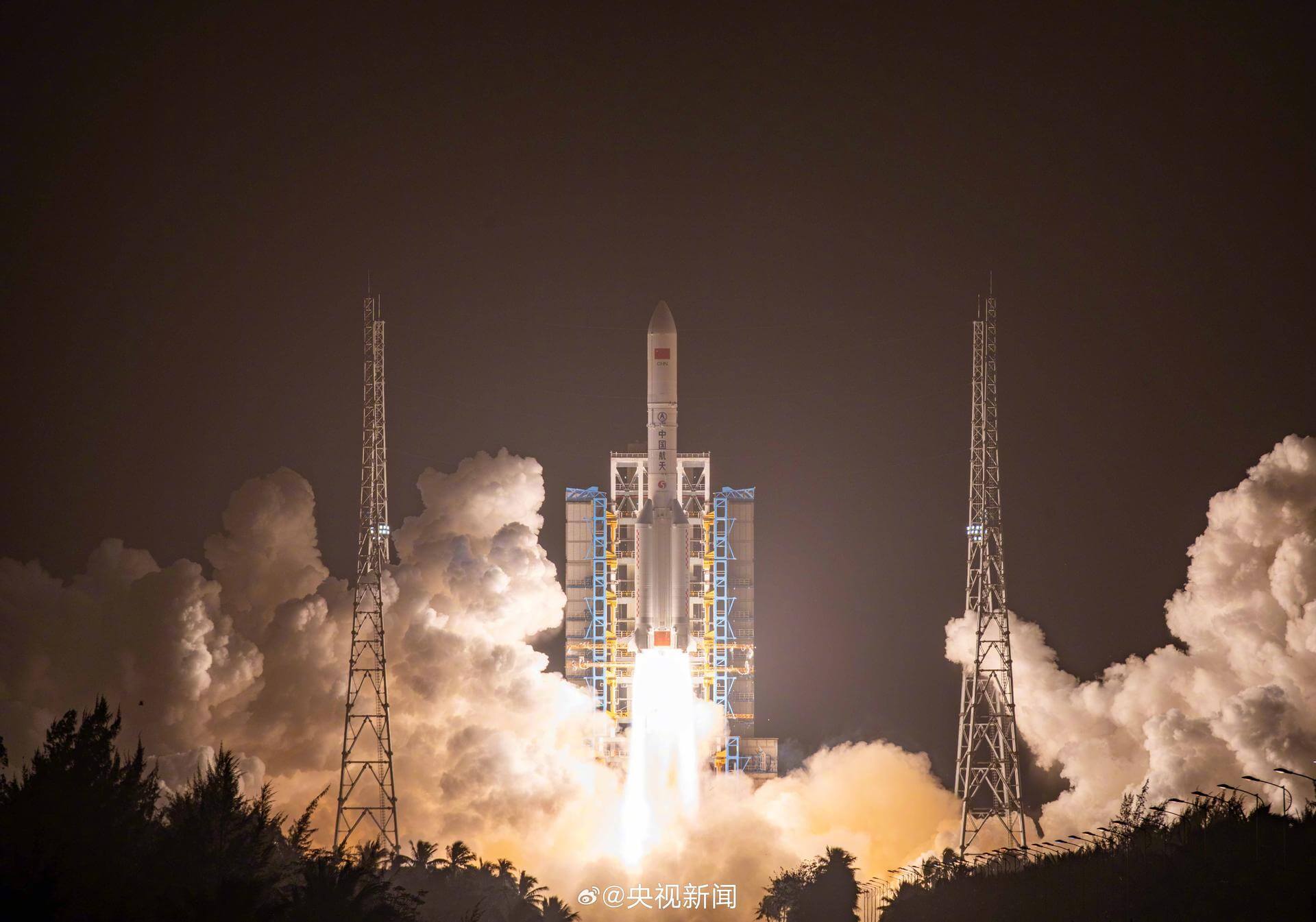
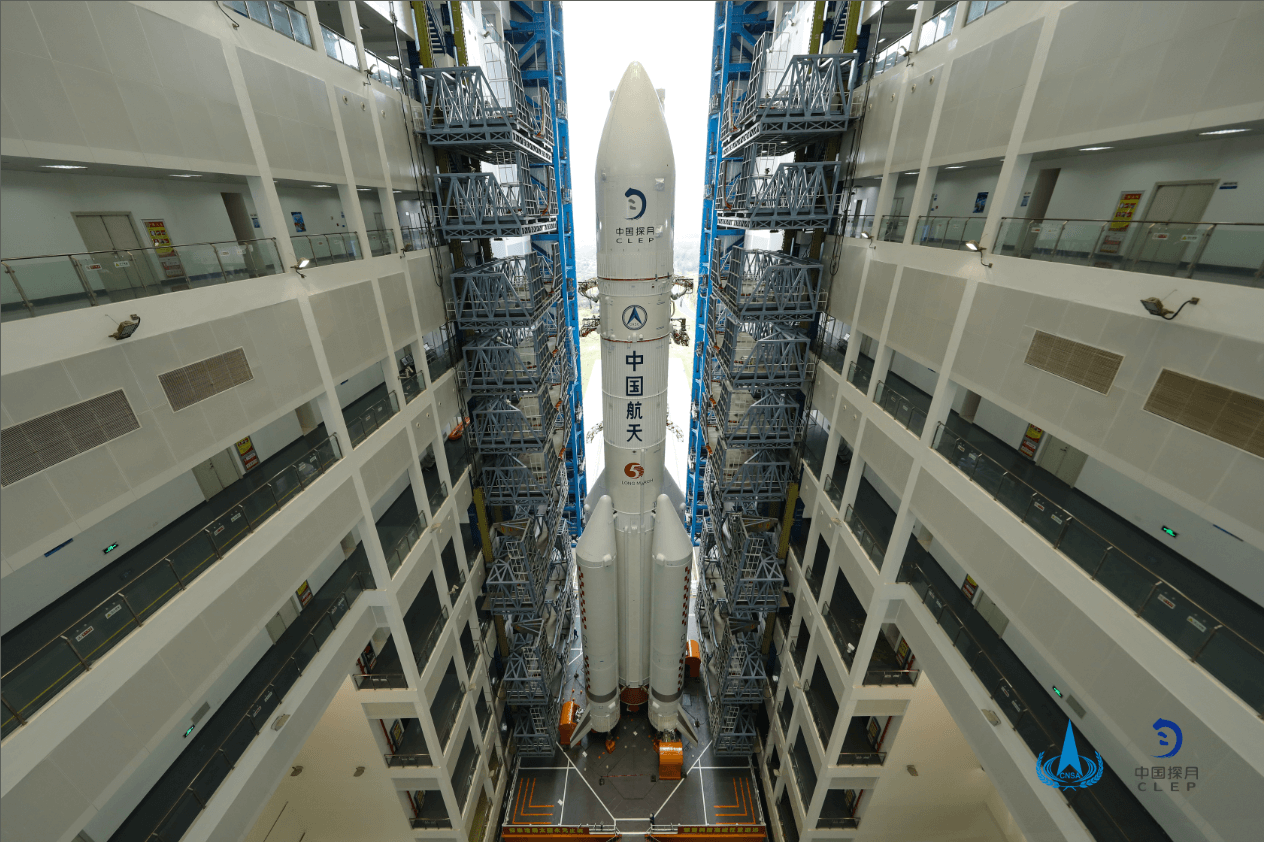
Long March 5
ActiveChina Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC)
Nov. 3, 2016
Description
Long March 5 is a Chinese heavy lift launch system developed by China Academy of Launch Vehicle Technology (CALT). CZ-5 is the first Chinese vehicle designed from the ground up to focus on non-hypergolic liquid rocket propellants. Currently, two CZ-5 vehicle configurations are planned, with maximum payload capacities of ~25,000 kilograms (55,000 lb) to LEO and ~14,000 kilograms (31,000 lb) to GTO. The Long March 5 roughly matches the capabilities of American EELV heavy-class vehicles such as the Delta IV Heavy.
Specifications
-
Stages
2 -
Length
57.0 m -
Diameter
5.0 m -
Fairing Diameter
― -
Launch Mass
867 T -
Thrust
10600 kN
Family
-
Name
Long March 5 -
Family
― -
Variant
― -
Alias
― -
Full Name
Long March 5
Payload Capacity
-
Launch Cost
― -
Low Earth Orbit
25000 kg -
Geostationary Transfer
Orbit
14000 kg -
Direct Geostationary
― -
Sun-Synchronous Capacity
―
China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation
Government
Chairman & President: Lei Fanpei
CASC 1999The China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC) is the main contractor for the Chinese space program. It is state-owned and has a number of subordinate entities which design, develop and manufacture a range of spacecraft, launch vehicles, strategic and tactical missile systems, and ground equipment. It was officially established in July 1999 as part of a Chinese government reform drive, having previously been one part of the former China Aerospace Corporation. Various incarnations of the program date back to 1956.
Upcoming Spaceflights
Long March 5 | Chang'e 7
China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation | ChinaWenchang Space Launch Site, People's Republic of China
TBD December, 2026
Status: To Be Determined
Mission:
Chang'e 7/CE-7 is scheduled to launch in 2026, including an orbiter, a lander, a mini-hopping probe, and a rover. The mission will land in the South Pole regions of the Moon to study lunar surface environment around the South Pole, especially in looking for water ice in lunar soil.
Lunar OrbitLong March 5 | Chang'e 8
China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation | ChinaWenchang Space Launch Site, People's Republic of China
TBD December, 2029
Status: To Be Determined
Mission:
Chang'e 8/CE-8 is scheduled to launch in 2028, including a lander, a rover and a legged robot. The mission will land in the South Pole regions of the Moon to study lunar surface environment around the South Pole and experimenting with resource utilization, including testing an enclosed terrestrial ecosystem in the lunar environment.
Lunar OrbitLong March 5 | Chang'e 6
China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation | ChinaWenchang Space Launch Site, People's Republic of China
May 3, 2024, 9:27 a.m.
Status: Launch Successful
Mission:
Chang'e 6/CE-6 is scheduled to launch in 2024 to return samples from the Far Side of the Moon (near southern edge of the Apollo Basin) for the first time. International science instruments from France, Italy, Sweden and Pakistan will also be on board.
Lunar OrbitLong March 5 | TJSW-11
China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation | ChinaWenchang Space Launch Site, People's Republic of China
Feb. 23, 2024, 11:30 a.m.
Long March 5 | Yaogan 41
China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation | ChinaWenchang Space Launch Site, People's Republic of China
Dec. 15, 2023, 1:41 p.m.
Long March 5 | Chang'e 5
China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation | ChinaWenchang Space Launch Site, People's Republic of China
Nov. 23, 2020, 8:30 p.m.
Status: Launch Successful
Mission:
Chang'e 5 is China's robotic lunar sample return mission, which is set to bring back at least 2 kg of lunar soils and rock samples. The probe will perform a soft landing on the Moon, then rendezvous and dock with the return module in lunar orbit and fly back to Earth.
Lunar OrbitLong March 5 | Tianwen-1 (Mars Global Remote Sensing Orbiter and Small Rover)
China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation | ChinaWenchang Space Launch Site, People's Republic of China
July 23, 2020, 4:41 a.m.
Status: Launch Successful
Mission:
Tianwen-1 ("questions to heaven") Mars mission includes a Martian orbiter and a lander/rover duo. This will be China's first mission to Mars. The spacecraft will reach Mars in February 2021. Lander will remain attached to the orbiter for two to three months before attempting its landing. The chosen landing area is Utopia Planitia, a huge basin formed by a large impact far back in Mars' history. The rover is expected to be in operation for about 90 Martian sols. The Tianwen-1 orbiter will provide a relay communication link to the rover while performing its own scientific observations for one Martian year. The orbiter will operate in a polar orbit in order to map Mars' morphology and geological structure while also using the Mars-Orbiting Subsurface Exploration Radar instrument to investigate soil characteristics and water-ice distribution. It will also measure the ionosphere and the electromagnetic and gravitational fields, the new paper reported. The rover will have 13 instruments detecting things such as topography, soil, environment, atmosphere, water ice, physical field and internal structure. It will investigate the surface soil characteristics and water-ice distribution with its own Subsurface Exploration Radar. It will also analyze surface material composition and characteristics of the Martian climate and environment on the surface.
Heliocentric N/ALong March 5 | Shijian 20
China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation | ChinaWenchang Space Launch Site, People's Republic of China
Dec. 27, 2019, 12:45 p.m.
Falcon 9
Starlink Group 6-58
Space Launch Complex 40 - Cape Canaveral, FL, USAA batch of 23 satellites for the Starlink mega-constellation - SpaceX's project for space-based Internet communication system.
Long March 4C
Shiyan 23
Launch Area 4 (SLS-2 / 603) - Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center, People's Republic of ChinaSatellite officially named for "space environment detection" purposes, exact details unknown.
Falcon 9
Starlink Group 8-2
Space Launch Complex 4E - Vandenberg SFB, CA, USAA batch of 20 satellites for the Starlink mega-constellation - SpaceX's project for space-based Internet communication system.
Long March 3
ZHTW 1-01
Launch Complex 2 (LC-2) - Xichang Satellite Launch Center, People's Republic of ChinaZhihui Tianwang 1-01 are 2 experimental Medium Earth Orbit communication satellites in a collaboration between Tsinghua University, SAST and the Shan…
Falcon 9
Starlink Group 6-56
Launch Complex 39A - Kennedy Space Center, FL, USAA batch of 23 satellites for the Starlink mega-constellation - SpaceX's project for space-based Internet communication system.